一、JSR107
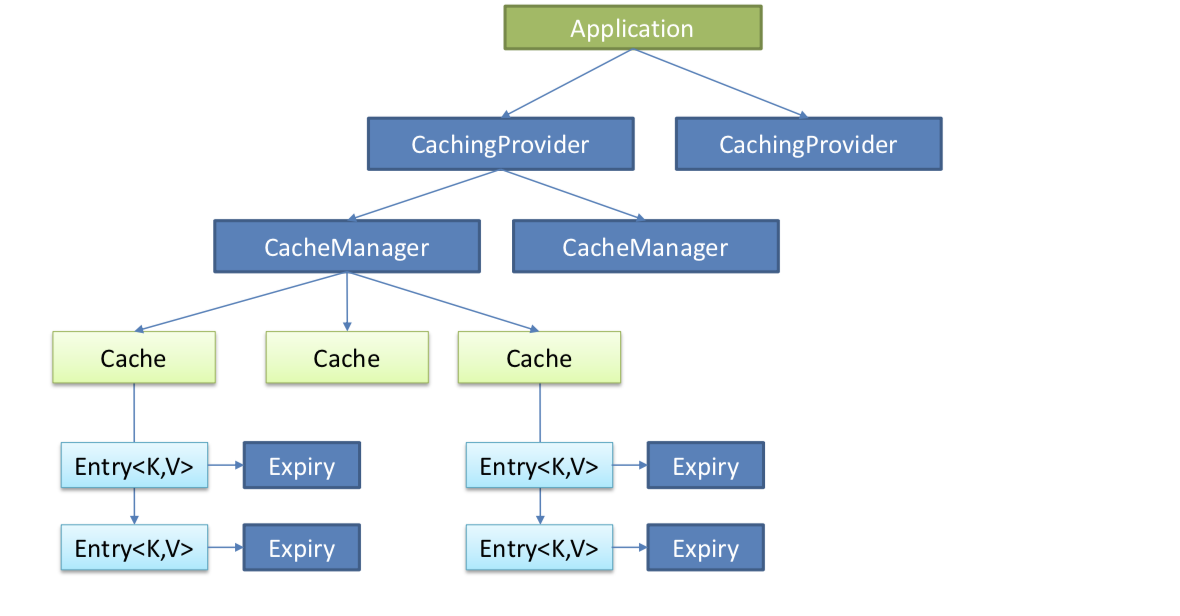
JSR107是Java的一套缓存规范,Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry 和 Expiry。
- CachingProvider:定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个CacheManager。一个应用可 以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
- CacheManager:定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache 存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
- Cache:是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个 CacheManager所拥有。
- Entry:是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
- Expiry:每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期 的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
二、Spring 缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache 和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager 接口来统一不同的缓存技术; 并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
- 默认使用 ConcurrenMapCacheManager
- Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
- Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等;
- 每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否 已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法 并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
- 使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
- 1、确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
- 2、从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据

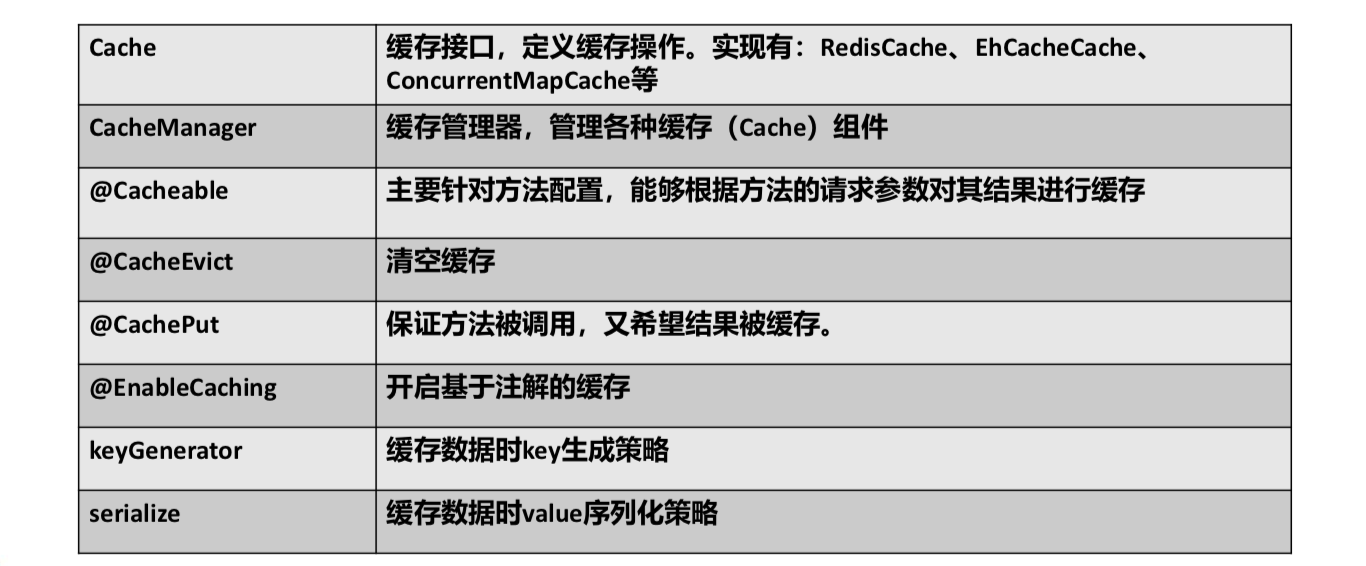
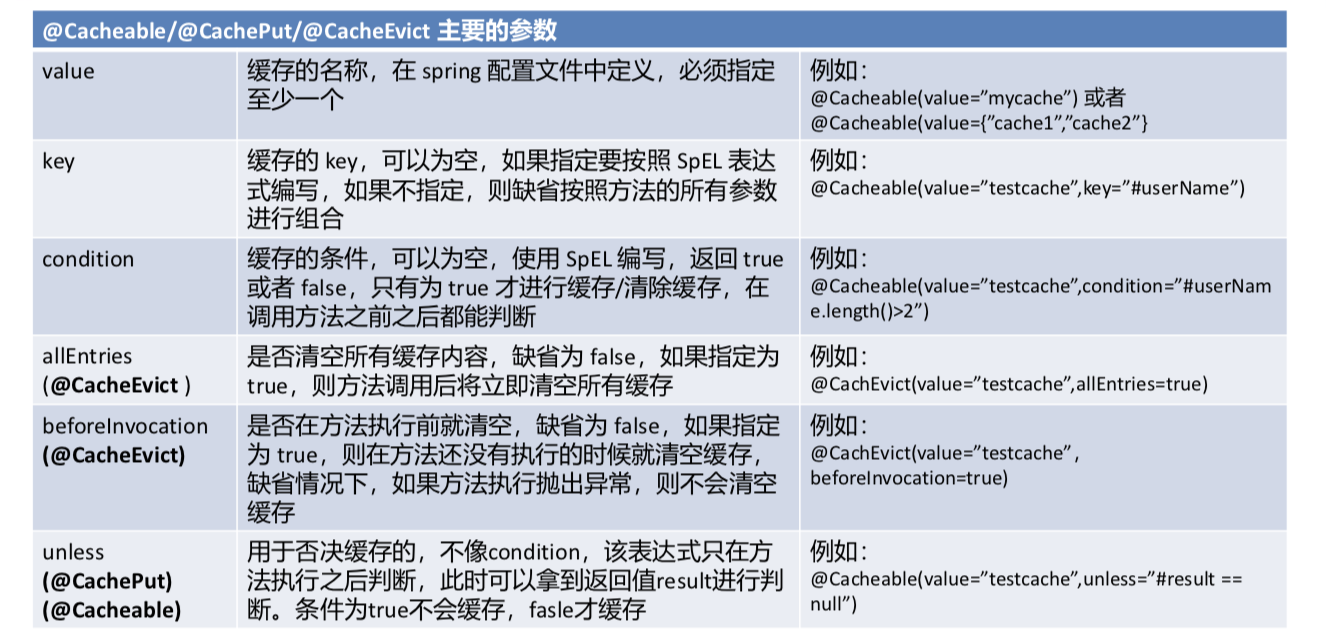
三、几个重要概念&缓存注解

四、整合redis实现缓存
创建项目springboot-cache,引入spring-boot-starter-cache、spring-boot-starter-data-redis 的依赖。
1. pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.gf</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-cache</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>springboot-cache</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.51</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.2</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity</artifactId>
<version>1.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2. RedisConfig
我们用redis自定义CacheManager,同时自定义序列化方式。
**注意:**lombok 的getter setter 和 编辑器生成的 getter setter,有时会存在差异。字段 dID ,编辑器生成的是 getdId() ,而lombok 编译成的是getDId(),这中情况会可能会导致序列化成json时多出一个字段 json串出现 did 和 dId ,出现这种情况时,对与该实体可以弃用lombok,手动生成来解决。
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer serializer = new GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer();
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().addAccept("com.gf.");
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer serializer = new GenericFastJsonRedisSerializer();
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().addAccept("com.gf.");
config = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(serializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager.RedisCacheManagerBuilder builder = RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory).cacheDefaults(config);
return builder.build();
}
}
3. EmployeeServiceImpl
@Service
public class EmployeeServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<EmployeeMapper, Employee> implements EmployeeService {
@Cacheable(value = "emp" , key = "#root.args[0]" , condition = "#id > 0" , unless = "#result eq null")
@Override
public Employee getById(Serializable id) {
System.out.println("getById");
return super.getById( id );
}
@Override
@CachePut(value = "emp", key = "#root.args[0].id", unless = "#result eq null ")
public Employee updateEmployeeById(Employee entity) {
boolean res = super.updateById( entity );
if (res){
return entity;
}
return null;
}
@CacheEvict(value = "emp", key = "#root.args[0]", condition = "#result eq true")
@Override
public boolean removeById(Serializable id) {
return super.removeById( id );
}
}
4. 启动类 SpringbootCacheApplication
使用**@EnableCaching**开启缓存
@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootCacheApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run( SpringbootCacheApplication.class, args);
}
}
之后我们通过postman测试。